Lesson 11 has three parts A, B, C which can be completed in any order.
In this exercise we will create four functions which perform geometric computations:
- a function to compute the length of a right triangle's hypotenuse,
- a function to compute the perimeter of a right triangle,
- a function to compute the distance between two points in 2D,
- and a function to compute the perimeter of an arbitrary triangle.
Hypotenuse
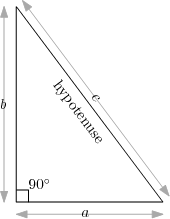 A right triangle is shown in the picture at the right-hand side. By definition, one of the angles of a right triangle equals 90 degrees (a right angle). The triangle has three sides. The side opposite the right angle has a special name: it is called the hypotenuse.
A right triangle is shown in the picture at the right-hand side. By definition, one of the angles of a right triangle equals 90 degrees (a right angle). The triangle has three sides. The side opposite the right angle has a special name: it is called the hypotenuse.
As shown in the diagram, let a and b denote the length of the sides adjacent to the right angle, and let c denote the length of the hypotenuse. The famous Pythagorean Theorem tells us that
In the first problem, your task is to convert this theorem into a function which, given a and b, computes the length of the hypotenuse.
Perimeter
Recall that the perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the sides. So in the diagram above, the perimeter has length a+b+c. Your program should assume that a correct version of hypotenuse has already been defined (you don't need to copy it from the first box to the second).
Distance in 2 Dimensions
To talk about points living in two dimensions, we specify them using two coordinates (the Cartesian coordinate system), the x coordinate and the y coordinate. We would like to write a function whose input is a pair of points, and whose output is the distance between those two points. It turns out that the hypotenuse function helps us perform this task!
In more detail, let the first point have coordinates (x1, y1) where x1 and y1 are real numbers, and let the second point have coordinates (x2, y2). The key idea is to draw the right triangle shown in the diagram below: the hypotenuse goes from (x1, y1) to (x2, y2) and so its length equals the distance between the two points.
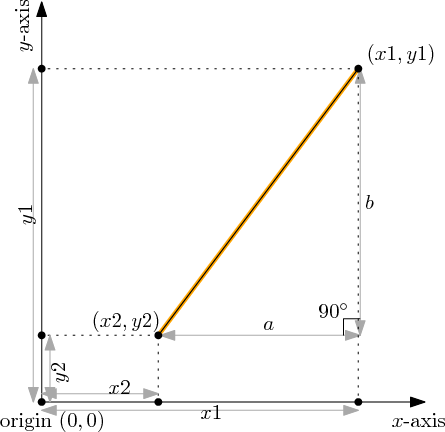
To calculate the length of the hypotenuse, we need to compute the length of the other two sides of the triangle. This can be done using the definition of coordinates (see the diagram): the horizontal displacement is a = x1-x2 and the vertical displacement is b = y1-y2.
Perimeter of Any Triangle
We now have the final exercise of this lesson. Remember that the perimeter is the sum of the three sides lengths of the triangle; and note that the side length is the same as the distance between two of the triangle's points.
You are now ready to continue to the next lesson!



